https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11363-6
Regular Article
Influence of temperature on the magnetic behavior of the Sb35.75Mn1.43Se62.82 compound
Solid State Physics Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, 12622, Giza, Egypt
* e-mail: mams411@gmail.com
Received:
17
September
2016
Accepted:
19
January
2017
Published online:
16
February
2017
Polycrystalline Mn-doped Sb2Se3 was synthesized by using the conventional solid-state reaction method. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of the prepared material in a fine-powder form were investigated. The elemental analysis of the prepared sample has led to the chemical formula Sb35.75Mn1.43Se62.82 indicating a nearly stoichiometric composition with a slight excess of Se. X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies revealed the presence of a predominant orthorhombic-type structure phase, the same as that of Sb2Se3, and an excess of selenium as a minor secondary phase. The optical absorption of the indicated sample was determined from the room temperature optical diffuse reflection data in the spectral range 400-2000 nm. The analysis of the optical absorption spectra revealed direct fundamental transition with an energy gap value of 1.18 eV. A symmetrical signal of the electron spin resonance (ESR) was obtained for the prepared ingot powder. The ESR spectrum reveals the Lorentzian shape of a broad single peak due to the Mn2+ - Mn2+ interaction with a Landé g-factor value of 2.00523. Magnetic properties such as magnetization 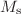 , coercivity
, coercivity 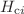 were affected by temperature under an applied magnetic field ranging from -20 to 20 kOe.
were affected by temperature under an applied magnetic field ranging from -20 to 20 kOe. 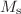 and
and 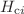 have values ranging from 0.1899 to 0.1226 emu/g and from 1.583 to 0.580 kOe, respectively with increasing temperature from 100 to 300 K. A positive shift of the hysteresis loops along the field axis was observed.
have values ranging from 0.1899 to 0.1226 emu/g and from 1.583 to 0.580 kOe, respectively with increasing temperature from 100 to 300 K. A positive shift of the hysteresis loops along the field axis was observed.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2017




