https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2013-13110-5
Regular Article
Automatic detection of lung nodules in computed tomography images: training and validation of algorithms using public research databases
Dipartimento di Fisica dell’università di Pisa and INFN, Pisa, Italy
* e-mail: niccolo.camarlinghi@df.unipi.it
Received:
11
July
2013
Revised:
12
August
2013
Accepted:
19
August
2013
Published online:
25
September
2013
Lung cancer is one of the main public health issues in developed countries. Lung cancer typically manifests itself as non-calcified pulmonary nodules that can be detected reading lung Computed Tomography (CT) images. To assist radiologists in reading images, researchers started, a decade ago, the development of Computer Aided Detection (CAD) methods capable of detecting lung nodules. In this work, a CAD composed of two CAD subprocedures is presented: 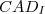 , devoted to the identification of parenchymal nodules, and
, devoted to the identification of parenchymal nodules, and 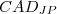 , devoted to the identification of the nodules attached to the pleura surface. Both CADs are an upgrade of two methods previously presented as Voxel Based Neural Approach CAD
, devoted to the identification of the nodules attached to the pleura surface. Both CADs are an upgrade of two methods previously presented as Voxel Based Neural Approach CAD  . The novelty of this paper consists in the massive training using the public research Lung International Database Consortium (LIDC) database and on the implementation of new features for classification with respect to the original VBNA method. Finally, the proposed CAD is blindly validated on the ANODE09 dataset. The result of the validation is a score of 0.393, which corresponds to the average sensitivity of the CAD computed at seven predefined false positive rates: 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, 2, 4, and 8 FP/CT.
. The novelty of this paper consists in the massive training using the public research Lung International Database Consortium (LIDC) database and on the implementation of new features for classification with respect to the original VBNA method. Finally, the proposed CAD is blindly validated on the ANODE09 dataset. The result of the validation is a score of 0.393, which corresponds to the average sensitivity of the CAD computed at seven predefined false positive rates: 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, 2, 4, and 8 FP/CT.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2013




